- Structural economic problems are often supply related, for example poor infrastructure or inadequate skills of labourers.
- Cyclical economic problems are often demand related, for example falling incomes and a low consumer confidence.
There are different types of macro economic policies aimed at addressing those problems:
- Fiscal policies are policies that involve the manipulation of taxes and expenses to achieve economic policy objectives.
- Monetary policies are policies that involve the manipulation of money supply and interest rates to achieve economic policy objectives.
- Regulation can also be used to influence economic growth. It is often assumed that less regulation reduces business costs and improves economic growth.
There are a number of influential economic views:
- Markets can deal with the issue (classical economics).
- The economy is often not operating at full capacity. The government can influence economic growth with spending and taxes (Keynesian economics).
- The central bank can influence economic growth with changes in money supply and interest rates (monetarism).
- People are not stupid and anticipate the effects of policy actions (rational expectations).
- Economic growth can best be achieved by lower taxes and less regulation (supply side economics).
There are a few alternative views:
- Fractional reserve banking causes economic booms and busts. Policy interventions aggravate those problems (Austrian School).
- Interest causes problems and international finance dominates communities and nations (community currencies, National Socialism).
- An unbalanced distribution of wealth can cause a revolution (socialism, Marxism).
- Economic growth is not sustainable (steady state economics, de-growth).
Classical economics
Introduction
According to classical economists, the economy tends to be at equilibrium at full employment because the desires of consumers exceed the capacity of the businesses to satisfy them. People produce in order to consume what they have produced or have acquired by exchanging what they have produced for what others have produced. This is reflected in Say's Law, which states that supply creates its own demand. When the economy is not in equilibrium at full employment, this is caused by a lack of price flexibility.
Classical economics suggests that everything will work out fine when markets are competitive and flexible so that prices can adapt fairly quickly. According to classical economics it is better that governments do not interfere with the economy, except for making markets more flexible and competitive. Unemployment is a consequence of inflexibility of the labour market. If markets have price flexibility then problems will resolve themselves quickly and recessions will be short lived.
Demand for goods and services
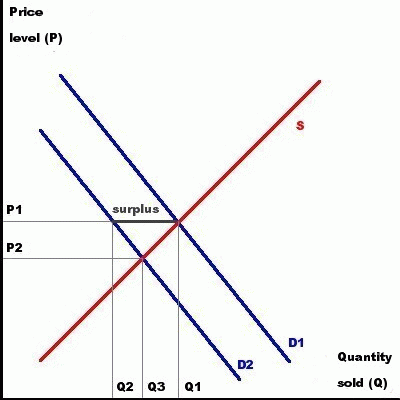
Classical economics assumes that if there is a surplus of goods or services, they will drop in price until they are consumed (see figure 1). Lower prices will make it more attractive to buy those goods and services while it be less attractive to produce them. Consumption will rise and production will drop and a new equilibrium will be achieved.
figure 1: quantity sold and price level
If
the demand for goods and services drops from D1 to D2, there will be
a surplus at price level P1 and only Q2 products will be consumed. As
long as prices have not dropped to P2, there will be a surplus of
products. After some time there will be a new equilibrium at a price
level of P2 and and a quantity of Q3. This may create a surplus of
labour.
Labour
supply and demand
Classical
economics assumes that if there is a surplus of labour, it will drop
in price until there is full employment (see figure 2). At lower
wages, working is less attractive so there will be less people
willing to work. At lower wages, it will be more attractive to hire
people so employment will rise at lower wages.
figure 2: labour supply and demand
If
the demand for labour drops from D1 to D2, the number of people
employed drops from N1 to N2 if the real wage level remains W1. As
long as the real wage level has not dropped to W2, there will be some
unemployment. After some time a new equilibrium has arrived at a real
wage of W2 and a number of people employed of N3.
The
value of money
When
prices drop, then the value of money rises. This means that the money
stock increases in the equation Money Stock (M) * Velocity (V) =
Price (P) * Quantity (Q). According to classical economics, people
will feel richer as a consequence and start to spend more and save
less. Even if they do not spend more in money terms and velocity does
not change, they spend more in real terms. Demand will rise again as
will employment.
Next Page 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15
(Note: You can view every article as one long page if you sign up as an Advocate Member, or higher).